We used Amazon SNS into one of our project where we need to receive instant updates to the various different microservices from other microservices. I was not able to find any good article which highlights everything about SNS integration into PHP or Laravel. This can be most confusing who is working with SNS for the first time. so I decided to write one which can help others. Following things are really important before we get started.
- What exactly SNS is?
- Where/When you can use it?
- How does it work?
- How to integrate it with PHP?
I will try to explain in a little bit brief here about SNS and will focus more on integration and problem that we tried to solve.
1. What exactly AWS SNS is?
AWS SNS stands for Amazon Simple Notification Service. It’s a distributed pub/sub messaging system for microservices. Where publishers can publish a message to different subscribers with various kinds of subscribers including SMS, HTTP Endpoints or Webhooks, Amazon SQS, Lambda, Mobile Push etc. We will cover HTTP only subscribers in this post.
Kind of pub/sub where the publisher can publish a message and multiple interested subscribers can subscribe to that. You can read more on the AWS Website Here.
2. When you need AWS SNS?
When your project is distributed into various microservices and if you need to communicate from one or multiple microservices to other microservices then SNS comes to play a really good role.
Our Problem:
In our case, our project contains 3 different systems, where authentication + user management is handled by one central system. But each system has its local users table, where minimal users data is cached for fast data retrieval and table joins. so it doesn’t need to query the central user system for each and every query.
If any new user is created by Admin on a central user management system, we need to notify other systems that a new user is created and they update their local users table.
3. How does it work?
Amazon SNS provides topics. You need to create a Topic and then define subscribers either programmatically or manually from Amazon Console. It depends on your use case. If you want to dynamically add subscribers then go that way or if you have some fixed microservices then you can define it from the console directly. This process works as follows:
- Create a Topic in AWS Console
- Create an HTTP subscriber
- SNS will send a SubscriptionConfirmation message to your HTTP Webhook
- Your microservice needs to call SubscribeURL
- Your subscription will be confirmed
This is the initial setup process. Once this is done. Everytime when any new message is published to Topic, it will call your webhook with that Message.
4. How to integrate it with PHP (Or any other PHP Frameworks like Laravel)?
Amazon has a very good PHP Library for their AWS products. Recently for SNS they have created another light-weight library to handle SNS Messages.
So we will use the following libraries in our integration.
- aws/aws-sdk-php – We will use this to publish a message
- aws/aws-php-sns-message-validator – To Recieve/Handle incoming message
Solution:
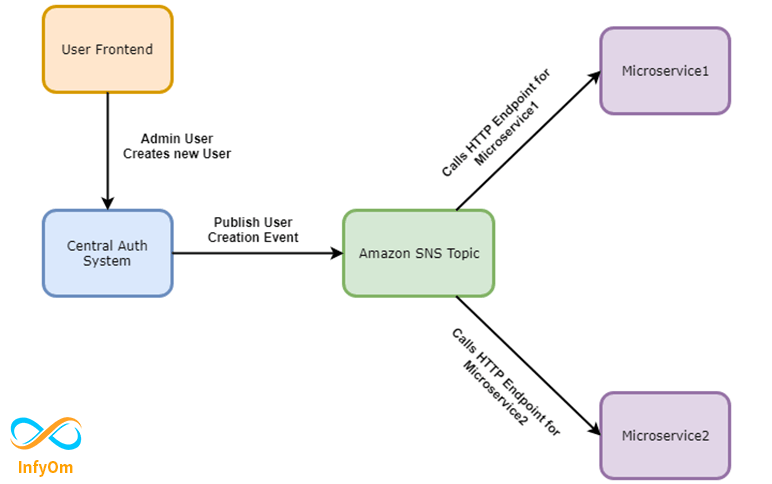
I will try to highlight the solution that we used to fix the above-mentioned problem. Check the following diagram:
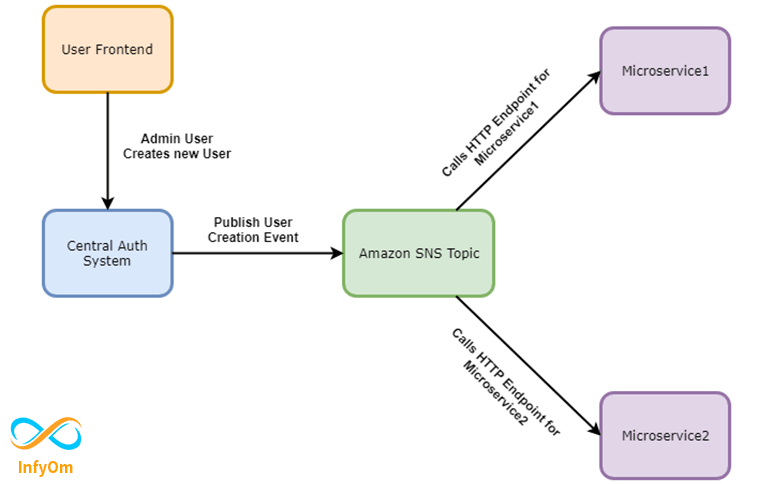
As you can see, we set up an SNS Topic and created two HTTP/HTTPS subscribers for two different microservices. When an admin user creates a new user into the system, we publish a message to SNS Topic which sends an update to both different microservices.
Now, let’s jump into the code.
Publishing a message:
You need to add aws/aws-sdk-php into your project. You can find installation steps on Github Repo. Also, you need to be familiar with AWS authentication process. These things are explained pretty well here. Collect all the things you need in terms of credentials.
- Key
- Secret
- Region
- Topic ARN
Following code hooked up into our central auth system. You can do this from wherever you want to publish your message. Create a client and then publish a message. You can pass two things into the SNS Message. Subject & Message body. Message body has several options. We will use a pure JSON string way for simplification.
use Aws\Credentials\Credentials;
use Aws\Sns\SnsClient;
$client = new SnsClient([
'version' => '2010-03-31',
'region' => $amazonRegion,
'credentials' => new Credentials(
$awsKey,
$awsSecret
)
]);
$subject = 'You got a new SNS Message';
$message = json_encode([
'message' => 'this is my first message via SNS Topic'
]);
$client->publish([
'TopicArn' => 'your-sns-topic-arn-here',
'Message' => $message,
'Subject' => $subject
]);
Generally, in our integration, what we did was, we used Subject to specify the type of event. Like Users.create, Users.update, Users.delete and Message used to contain user information. You can customize it based on your use-case.
That’s it. Your message is published to a topic.
Handle Incoming SNS Message:
To handle SNS messages we need to integrate aws/aws-php-sns-message-validator into our project.
SNS will call our webhook for multiple kinds of events. It comes with Type param into the message body.
- SubscriptionConfirmation
- Message
- UnsubscriptionConfirmation
Based on the Type parameter, we need to take relevant action. We have used the following code into our microservice webhook handlers.
use Aws\Sns\Message;
use Aws\Sns\MessageValidator;
try {
// Retrieve the message
$message = Message::fromRawPostData();
// make validator instance
$validator = new MessageValidator();
// Validate the message
if ($validator->isValid($message)) {
if ($message['Type'] == 'SubscriptionConfirmation') {
// if it's subscription or unsubscribe event then call SubscribeURL
file_get_contents($message['SubscribeURL']);
} elseif ($message['Type'] === 'Notification') {
$subject = $message['Subject'];
$messageData = json_decode($message['Message']);
// use $subject and $messageData and take relevant action
}
}
} catch (Exception $e) { // Handle exception .
}
As you can see, based on Type, we are performing different operations.
This way, all our microservice can communicate in a very effective and highly available way to each other. Hope this helps :).