Testing Posts
Use case Testing: What is Use Case Testing and How to Prepare Testcase ?Testing

Use case Testing: What is Use Case Testing and How to Prepare Testcase ?Testing
What is Use Case Testing and How to Prepare a Test Case for Testing?
In the phases and life cycle of software development, use case plays an important role. The entire process depends on the actions of the user and the response by the system to the actions. Hence it can be seen as documentation of the actions which is performed by the user or actor and then the corresponding interaction by the system to those actions. Not all the use cases result in achieving the goal by a user to the interactions with the system.
In a use case, the system responds to the situation or behavior. It is user-oriented rather than system-oriented. That is, they are actions that are done by the actor/user and not the output produced by the system. Hence the development team writes the ‘use cases’ as this phase depends on them. The writer of use cases, a team of development, customers, all of them together contribute towards the creation of use cases and testing.
What is Use Case Document?
Use case documentation helps to complete an overview of all the several ways in which the user interacts with the system to achieve the desired objective. The documentation will help to check the requirements for the software system and what is lacking in this process.
Who will use the Use Case Document?
As the documentation helps to get an overview of ways in which users can interact with the system, better documentation is always required for easier results. This documentation will be useful to the software developers and software testers along with the stakeholders.
There are several types of uses for these documents. It helps developers to implement the code and design the same. Further, testers use them to create test cases. Business stakeholders, on other hand, use the documentation in order to understand how the software works and their respective requirements.
Elements in Use Case Testing
The major elements of the use cases are brief introductions which help to explain the case.
- Actor, that is, the users which are involved in use case actions.
- Precondition, which is the conditions that need to be satisfied before the case begins.
- Basic Flow, or the main scenario which is a normal workflow in the system. In other words, this is a flow of transactions done by actors to accomplish their goals.
- Alternate flow, which is a less common interaction done by an actor with a system
- Exception flow, which prevents a user from achieving the goal
- Postconditions that are required to be checked after the case is finished.
How to Prepare Test cases?
It is best if the test cases for the main scenario are written first and then written second for alternate steps. These steps in test cases are from use case documents. Cases are supposed to be required as steps and the user or actor must be able to enter the same. Test design techniques can be used and developed to help reduce the number of test cases which can help reduce the time taken for testing.
Writing test cases and testing is an iterative process. Practice and knowledge of domain and system are required in this case. Using case testing in applications can be used to find missing links and incomplete requirements. Finding and modifying the same will bring efficiency and accuracy into the system domain.
Main QA points for delivering high-quality SaaS-based solutionsTesting

Main QA points for delivering high-quality SaaS-based solutionsTesting
SaaS testing is the process of conducting a test case on an on-demand software or web-based software system. Software testing as a service is different from testing on-premises applications because SaaS-based application testing requires access to browsers and is centered around web application testing methods.
The software tests robust SaaS performance testing plans against real-world traffic in a cloud environment to confirm that the service is available, useful, and optimized for all web concurrent users at all times. By adhering to the best practices of SaaS testing, your team can quickly deploy updates and upgrades, increase ROI, and increase user satisfaction.
SaaS-Based Solutions: 4 Reasons to Testing
Reason 1. Smart scalability
The option to change software capabilities immediately upon request allows tenants to save costs on using cloud services. What's more, SaaS vendors use auto-scaling mechanisms that diagnose the amount of current users and adjust the software according to sizing needs.
Reason 2. Regular and rapid updates
Within the tight relationship with the SAS provider, the shortcomings and modifications of all solutions go through it. As a rule, the process of correcting errors and making changes is quick and frequent. Therefore, a robust QA strategy should be defined to optimize the snowfall of test scenarios on short notice.
Reason 3. Multi-tenancy
SaaS opportunities to use shared cloud resources make it affordable for a range of different organizations and streamline software support. Within the approach of providing access to multiple customers, each tenant's data is different and remains invisible to other subscribers. However, the sheer number of connections with a vendor can cause difficulties in compatibility and integration. In this case, improving the quality of the API may be the escape solution.
Reason 4. Adjustable architecture
One more reason why companies choose SaaS is the ability to customize and specify settings that perfectly match the needs of the business. And this requires thorough supervision, as improper operation of the IT solution can lead to defects after adding some modifications that can exacerbate the increased churning rate.
Therefore, in these specifications, SaaS testing is more complex than testing cloud and on-premises apps, which gathers more demand and a more in-depth attitude towards QA activities.
Now Let's see main points to get Upscale SaaS-Based Solutions
1. Functional testing
Testing all levels of connections between IT product components, including units, their integration and system testing, QA experts check the proper management of efficiency. Notably, the general requirements include numerous cases corresponding to casual user scenarios. Checking numerous configuration combinations makes testing more complete.
2. Performance testing
While on-premises applications are based on the user's environment, the customer experience in SaaS-based products may be influenced by others. Thus, performance checks are necessary - to run stress and load tests, QA engineers identify the above limitations of software capability and evaluate its behavior under the expected number of concomitant users.
3. Interoperability testing
SaaS based products perform flawlessly against various browsers and platforms as a prerequisite. Before conducting the interoperability test, the QA team estimates the most preferred browsers and platforms and isolates the browsers used by a few clients to exclude them. With every browser or platform tested, QA specialists cover the full scope of test configuration and provide seamless software operation for a wide range of users.
4. Usability testing
Intending to reduce churn rates and build long-term relationships with end users, companies primarily strive to enhance the customer experience with convenient app usage. By providing simple information architecture, simple workflow and interaction as well as visual readability and adequate feedback on commonly used functions, the individual can satisfy customers through a user-friendly application.
5. Security testing
Within sensitive data, SaaS-based solutions need to enable highly secure storage and disposal of information. Accepting casual accounts and roles, these applications require full validation of access control. To identify vulnerabilities and avoid data breaches, QA experts perform penetration testing, exploring potential barriers.
6. Compliance with requirements
Winning the competition also assumes meeting worldwide standards. Depending on the industry, HIPAA checklists for health products, OWASP security recommendations for any-domain web and mobile applications, GDPR to enable secure data storage and worldwide transfers and much more may be required to conduct software testing.
7. API testing
API testing is required between organizations delivering SaaS products, in conjunction with customer platforms and other third-party solutions. With it, instead of using default user inputs and outputs, QA engineers run positive and negative views of calls on APIs and analyze responses to system interactions. Such an approach allows in advance to ensure that the API application and the calling solution work properly. It focuses primarily on the business logic layer of software architecture.
8. Regression testing
Once the new functionality is implemented, it needs to be verified that the latest improvements have not affected the developed features. Being an elaborate and cumbersome process, the SaaS regression test includes all the test types mentioned above and a range of test cases involving more.
InfyOm has experience delivering comprehensive QA assistance with solid regression testing. Learn how our QA engineers tested and streamlined the software, ensuring the quality of the SaaS platform for public housing authorities.
Summary
Once you decide to build a true bug-free SaaS application, IT strategy needs to add SaaS testing to its specifications that include the use of Wise Cloud resources, prompt updates, multi-tenancy and customization.
By introducing QA tips from the InfyOm list, one can improve the quality of solutions, obtain the required business and operational values, and reduce churning rates.
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Why it matters and how to test for it?Testing

Cross-Browser Compatibility: Why it matters and how to test for it?Testing
Cross-browser testing means to ensure these components function seamlessly across all targeted browser versions. You can use it to ensure HTML, JavaScript, Applets, AJAX requests, Flash, and web design elements all look and behave as intended on every individual browser type. The overarching goal of cross-browser testing is to provide uniformity by enabling testers to detect bugs that might prevent a site from displaying or functioning properly across various screen dimensions and browsers.
Why Is Cross-Browser Testing Important?
Although it’s one of the biggest time-grabbers for QA and development teams, cross-browser testing is essential for delivering the best experience possible to users. Browser vendors follow Open Web Standards, but they have their own interpretations of it. Since they each render HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in unique ways, thoroughly debugging your website’s source code is not enough to ensure that your website will look and behave as intended on different browsers (or different versions of a single browser). So it falls to web developers to abstract browser differences. Cross browser testing helps with that by pinpointing browser-specific compatibility errors so you can debug them quickly. It helps ensure that you’re not alienating a significant part of your target audience–simply because your website does not work on their browser-OS.
Which types of issues facing in cross-browser testing?
- Different JavaScript implementation
- Missing CSS resets
- Font size and image orientation mismatch
- No support for HTML5
- Inconsistent page alignment
- Layout incompatibility with browser
- Mismatches in frameworks or library versions
What Measures Are Involved in Cross-Browser Testing?
Compatibility testing includes everything, but you may not always have the time for that. To do it right, product teams constrain their testing with a test specification document (test specs) which outlines broad essentials—a list of features to test, what browsers/versions/ platforms to test on in order to meet the compatibility benchmark, test scenarios, timelines, and budget.You can categorise the features that will undergo testing like this:
- Base Functionality: To ensure that basic functionality works on most browser-OS combinations. For example, you could be testing to verify that:
- All dialogs boxes and menus are working as intended
- All form fields accept inputs after validating them correctly
- Website handles first-party cookies (and features like personalisation that are dependent on them) correctly seamless touch input for mobiles or tablets.
- Design: This ensures that the website’s appearance—fonts, images, and layout—matches the specifications shared by the Design team.
- Accessibility: Accounts for compliance with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to enable differently-abled users to access the website.
- Responsiveness: Verifies that design is fluid and fits different screen sizes/orientations.
Harmful Browser Security Threats: How to Avoid Them? -2Testing

Harmful Browser Security Threats: How to Avoid Them? -2Testing
In our previous tutorial, we had seen the most common security threats. Let's see Main Seven Tips and its Recommendations on How You Can Protect Yourself from These Threats are mention below.
1. Saved Login Credentials
It is recommended not to save credentials in the browser. Instead, use password managers like Password Safe and KeePass to store credentials.
Password managers work through a central master password and help you keep your website passwords secure.
You can also set the administrator to access a saved login or URL, depending on your convenience and security reasons.
2. Removable Browsing History
Deleting the browser cache is a way to remove risky information, especially when engaging in confidential activities such as online banking. This step can be performed manually in the browser or set to automatic when the browser is closed. Another way to stay protected from this threat is to use Incognito or Private Browsing mode, where no saves can be harvested.
3. Disable Cookies
The best solution to the threat of cookies is to disable them when using your browser.
However, it is not exceptional, as many websites rely on cookies and thus get limited access to their functionality once they are turned off.
Disabling cookies may also result in annoying prompts. Getting rid of cookies on a periodic basis can help you protect your browser, beware of duplicate information by websites as a side effect of it.
4. Reduce Browser Cache by using Incognito Mode
Protection from such threats can be achieved through incognito browsing as well as by manually clearing the cache as per the requirement, especially after a sensitive browser search.
5. Look for Standard Java Configuration
Java is a widely used language for running Windows and other operating system-related code. It is designed in such a way that the applets inside it run in a separate sandbox environment, which helps prevent them from accessing other operating system components and applications. But more often than not, these vulnerabilities allow small applications to escape from the sandbox environment and cause the threat.
To avoid Java-related threats, search and choose a standard Java security configuration that works best with your browser as well as PC and deploy these configurations through a key source such as Group Policy.
6. Third-Party Plugins or Extensions
Browsers often have third-party add-ons or extensions provided for various tasks, for example, JavaScript or Flash for viewing or working with content. These are both from well-known high-quality dealers, however, there are various modules and add-ons from less legitimate sources and may not, however, offer a business-related benefit. For this type of threat, it is recommended to only allow business-related plugins and extensions as a key aspect of the official business approach, for example, to use the Internet and email. Depending on the browser(s) used in your link, explore ways to whitelist unwanted plug-ins or appropriate plug-ins, so that only those plug-ins can be served. Security modules are arranged for automatic updating or submission of new forms by focused components, (for example, Active Directory Group Policy or System Center Configuration Manager).
7. Ads Popping up and Redirects
Pop-up ads are well-known malicious ads that can be particularly confusing and difficult to work with. They regularly give false notifications, for example, they confirm that PC you have an infection and encourage you to submit their antivirus to activate it. Usually, malware is the thing that really ends up happening. These popups are questionable to close because often there is no X to do it like this.
The best alternative is to close the program completely or use Task Manager in Windows / Execution direction in Linux to close the application.
That's it. If you want to harm-free system, take these tips and apply them to your Web-application. It will help to protect from security threats.
What is Agile Testing Methodology & How it Works?Testing

What is Agile Testing Methodology & How it Works?Testing
Agile testing is a software testing process that follows the principles of agile software development. Agile testing methodology aligns with iterative Development Methodology in which requirements develop gradually from customers and testing teams. The development is aligned with customer requirements.
The agile testing process is a continuous process rather than being sequential. The testing begins at the start of the project and there is ongoing integration between testing and development. The common objective of agile development and testing is to achieve high product quality.
Agile Testing Methods
Behavior Driven Development
Behavior Driven Development (BDD) improves communication amongst project stakeholders so that all members correctly understand each feature before the development process starts. There is continuous example-based communication between developers, testers, and business analysts.
Acceptance Test Driven Development
ATDD focuses on involving team members with different perspectives such as the customer, developer, and tester. Three Amigos meetings are held to formulate acceptance tests incorporating perspectives of the customer, development, and testing. The customer is focused on the problem that is to be solved, the development is focused on how the problem will be solved whereas the testing is focused on what could go wrong. The acceptance tests are a representation of the user’s point of view and describe how the system will function. It also helps to verify that the system functions as it is supposed to. In some instances acceptance tests are automated.
Exploratory Testing
In this type of testing, the test design and test execution phase go hand in hand. Exploratory testing emphasises working software over comprehensive documentation. The individuals and interactions are more important than the process and tools. Customer collaboration holds greater value than contract negotiation. Exploratory testing is more adaptable to changes. In this testers identify the functionality of an application by exploring the application. The testers try to learn the application, and design & execute the test plans according to their findings.
Agile Testing Life Cycle
The agile testing life cycle includes the following 5 phases:
-
Impact assessment - Gather input from stakeholders and users, this will act as feedback for the next deployment cycle.
-
Agile Testing Planning - All stakeholders come together to plan the schedule of the testing process, meeting frequency, and deliverables.
-
Release Readiness - In this stage, we review the features that have been developed/implemented are ready to go live or not.
-
Daily Scrums - Daily standup meeting includes everyday meetings to catch up on the status of testing and set the goals for the whole day.
- Agility Review - Weekly review meeting with stakeholder meeting to review and assess the progress against milestones.
Conclusion
Agile testing not only facilitates the early detection of defects but also reduces the cost of bugs by fixing them early. This approach also yields a customer-centric approach by delivering a high-quality product as early as possible.
Harmful Browser Security Threats: How to Avoid Them?Testing

Harmful Browser Security Threats: How to Avoid Them?Testing
Web browser, is the most used application or portal for users to access the Internet. These browsers are very advanced, with improved usability and ubiquity. The individual is exposed to different internet browsers. Each of them consists of some perceived and real benefits. However, it is also true that none of them are safe from security threats. In fact, website browsers are more vulnerable to security vulnerabilities and when users interact with websites, they carry the possibilities of malware and other threats in them.
Mainly, 5 most common browser security threats and how to protect your system
With that in mind, here are some of the most common browser security threats and how to protect your system from them are follow below:
1. Removing Saved Login Credentials
Bookmarks associated with saved logins for linked sites is a terrible combination and doesn't really favor your system. When this is done, a hacker with little knowledge can hack it. There are some websites that use two-factor authentication, such as sending OTPs to your mobile phone to access them. However, many of them use this as a one-time access token so that a person can confirm his or her identity on the system they are intended to connect from. Deleting saved credentials is not good for your browser as well as for your system in general. Cybercriminals A can easily reset important identifiers and profiles on almost every website you visit. They can do this from anywhere and at any time. Once they have your IDs and passwords, they can run them from any system of their choice.
2. Permission to Browser History
Your browser's browsing history is a type of map or mechanism that keeps track of what you're doing and what sites you're visiting. It not only tells us which sites you visited, but for how long and when as well. If a criminal wants to get your credentials from the sites you access, they can do so easily, knowing which sites you have accessed through your browsing history.
3. Cookies
Cookies made up of locally stored files that identify association with certain files are another common browser security threat. Similar to browsing history, it can also track the site you visit and get credentials.
4. Browser Cache
Browser cache consists of storing sections of website pages which makes accessing and loading sites easier and faster, every time you visit. This can also identify the site or portal you have accessed and the content you have gone through. It also saves your location and device detection, making it a risky item as anyone can identify your location and device.
5. Autofill Information
Autofill information can pose a huge threat to your browser. Browsers like Chrome and Firefox store your address information, sometimes your profile information, and other personal information. But are you prepared if you fall into the wrong hands? Isn't it? Well, the criminal is now aware of and privacy to all your personal details.
In our next tutorial, will see Tips and Recommendations on How You Can Protect Yourself from These Threats.
How to test reCAPTCHA form - prepare yourself for bots !Testing

How to test reCAPTCHA form - prepare yourself for bots !Testing
Nowadays, people are hacking secure data systems, so will See the security testing criteria for reCAPTCHA forms.
reCAPTCHA is a technology that assesses the probability that the entity that uses your web code (page, app, portal, etc.) is a human and not a bot (or the other way around). Grabbing information of behavior (of a user or a bot) encapsulates it in the token that gets sent to your server. On your server, the token is being sent again to Google for returning the assessment on how probable it is that the token was generated by a human. Part of the response returned from Google to your server:
Let's See the points how to Test 🛠️
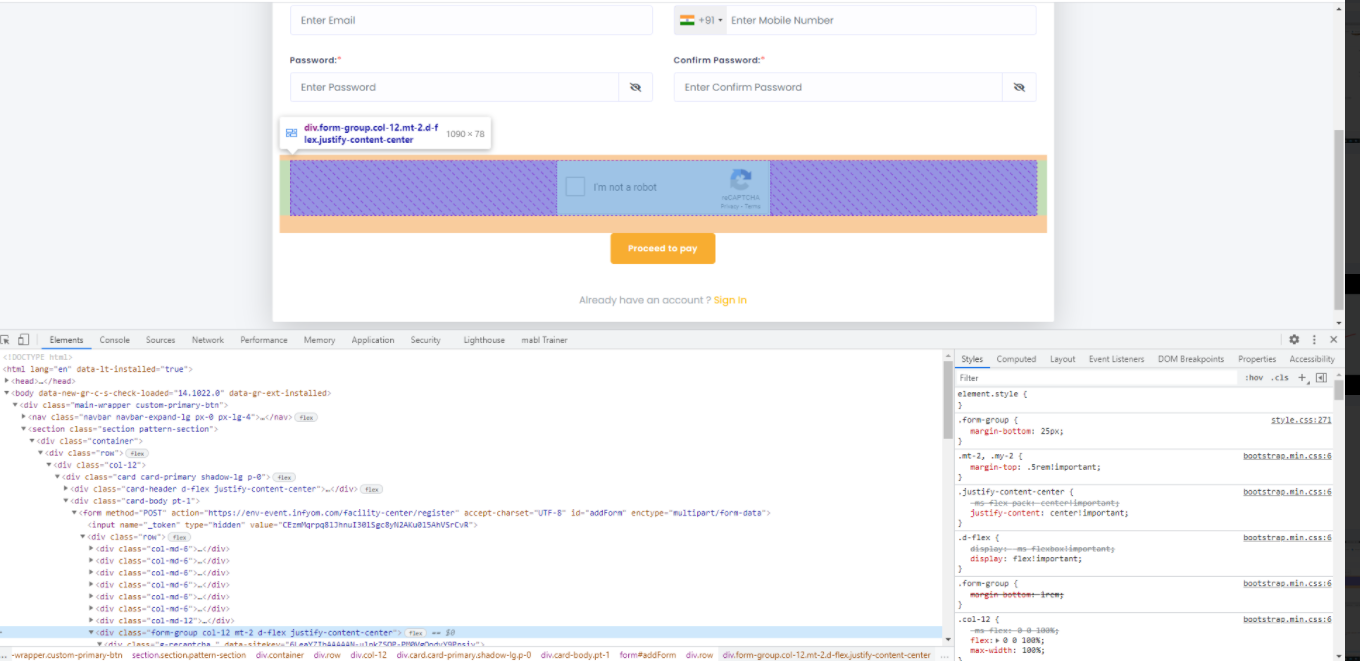
First, we validate from the frontend
On any reCAPTCHA from removing that div from inspect element and then trying to save, there must be valid and records should not store on the backend as shown in the image.
Remove this div then save the form there should be a validation message for reCAPTCHA verification and the form should not be saved, if the form is submitted then the data were stored in the data table which was False to the system.
Now Let's see how we validate from the postman
First, add testing form URL on browser and apply Post method and on body add all fields which are added in form lets see on the image.
Now add on the header at Key column CSRF token, X-Requested, cookie and add its perspective value as shown in the image.
CSRF token and XSRF-TOKEN will store in the cookie which will get from the front page from inspect element.
Now, click on send request and validate the status should be false as shown in the image
If the status changes to true, then the data stored in a table & will create a problem, and the reCAPTCHA form will validate false.
Hence, reCAPTCHA form Test, Hope this helps.
Performance Testing Part-1Testing

Performance Testing Part-1Testing
What is Performance Testing?
Performance testing, which is a non-functional testing method performed to determine system parameters in terms of responsiveness and stability under various workloads. Performance testing measures the quality characteristics of a system, such as a scalability, reliability, and resource use.
Types of Performance Testing
There are mainly six types of performance testing Let's see in detail.
Load Testing
It is the simplest form of testing conducted to understand the behavior of the system under a specific load. The load tests will determine the measurement of important business-critical transactions and will also monitor the load on the database, application server, etc.
Stress Testing
It is performed to find the upper limit capacity of the system and also to determine how the system is operating if the current load greatly exceeds the expected maximum.
Spike Testing
The Spike test is performed by suddenly increasing the number of users by a very large amount and measuring system performance. The main objective is to determine whether the system will be able to carry the workload.
Scalability testing
It Measures performance based on the software's ability to increase or decrease performance measurement attributes. For example, a scalability test could be performed based on the number of user requests.
Volume Testing
Under large test volume no. From. The data is filled in a database and the overall behavior of the program system is monitored. The goal is to check the performance of the software application under different database sizes.
Endurance Testing
It is done to make sure the software can handle the expected load over a long period of time.
We will see full performance testing process points in our next article, to continue...